Effective management of accounting reconciliation break is crucial to ensure the financial health, regulatory compliance, and reputation of a company. Discrepancies, whether related to non-matching transactions or input errors, can significantly impact an organization’s operations and profitability.
In this article, we will explore the financial risk associated with managing accounting reconciliation break and the benefits of automating this process. Additionally, we will introduce the new version of Calixys’ reconciliation platform, XREC, which offers advanced features to automate the detection, processing, and classification of discrepancies, thereby enhancing the efficiency and accuracy of reconciliation processes.
Break management refers to the process by which financial services reconcile records between external systems (e.g., bank statements) and accounting records. For instance, in bank reconciliations, all recorded transactions at the accounting and bank levels must be compared. If all transactions match in terms of data (amount, date, description, etc.) and are present in both systems, it’s a perfect match.
However, when transactions are missing in one system or the other, or if they don’t match exactly, discrepancies arise.
There are two types of discrepancies:
“False” discrepancies, which are often due to :
“True” discrepancies, which are often due to the :
Once detected, discrepancies must be resolved to ensure account perfect balances. If there is an input or calculation error, it must be corrected, or at the very least, justified in case of an audit.
The second step is to analyze discrepancies. Once automatically detected, they must be isolated, analyzed, and classified. For each discrepancy, it must be determined whether it’s a duplicate, a missing entry, or an orphan, for example, through comparative identification.
Regular and diligent discrepancy management ensures a company’s financial health, its reputation, and also helps detect fraud and process flaws. Moreover, excessive discrepancies often lead to significant financial losses for companies, making it a matter of profitability.
While it’s challenging to provide an exact figure for the cost to a company of not managing or managing reconciliation breaks poorly, as it depends on various factors (company size, industry, nature, and extent of discrepancies, etc.), the following elements can be considered :
Therefore, it is essential for companies to establish robust accounting reconciliation processes to avoid these potential costs. Specific costs will vary from one company to another, but poor management of reconciliation discrepancies can have significant financial repercussions. Based on our experience and depending on the size of the company and its industry, the average annual cost can reach hundreds of thousands of euros. And in the banking sector, this figure can easily be multiplied by 2, 3, or more, depending on whether it’s a private house or a public institution. These financial losses have long been part of an accepted loss tolerance by companies. As of now, and thanks to automation replacing manual verifications, companies can significantly reduce these losses.
Automating reconciliation break management offers numerous benefits for companies :
In summary, automating accounting reconciliation break management allows companies to improve compliance and accuracy while freeing up time and optimizing resource usage.
Calixys is launching a new version of its automated platform, XREC.
XREC is a SaaS solution developed by the Calixys team, aimed at helping companies automate and ensure the reliability of their reconciliations with a powerful and precise algorithm.
In this new version, the Calixys team aimed to further enhance the tool’s performance by being more attentive to user needs and offering even more adaptability. This new version includes :
Automatically identifying discrepancies rather than doing it manually saves considerable time and efficiency. But with this new XREC version, the Calixys team wanted to go further.
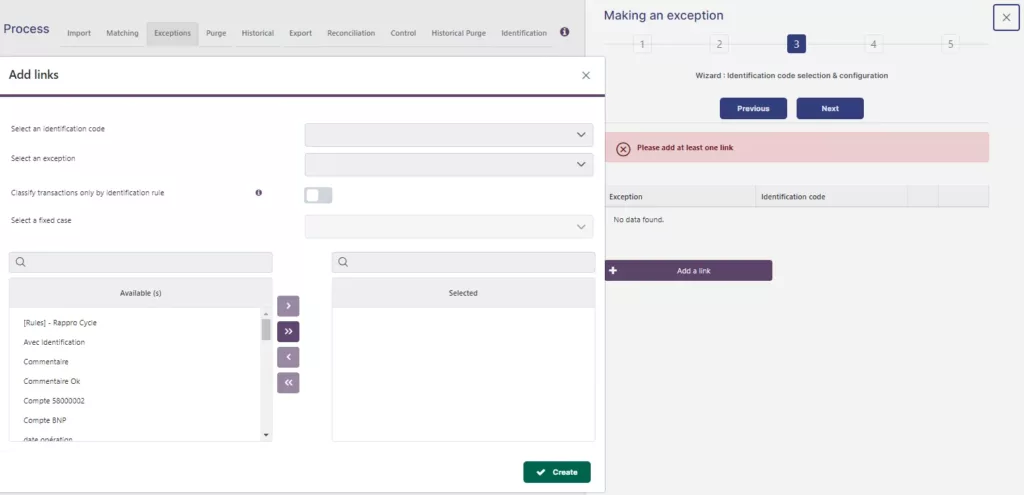
In addition to detecting discrepancies, the solution now allows for automatic handling and classification of exceptions. Once discrepancies are identified, they can be set aside for analysis and classification.
Let’s take the example of a transaction reconciliation :
It is not only possible to know which transactions are not matched and the unique or cumulative amount of these discrepancies, but also to know what type of discrepancy it is thanks to pre-defined exception rules. When a transaction reconciliation presents a discrepancy, it is possible to determine whether it’s an orphan, a duplicate, an error, etc.
Step 1: Create identification rules on the platform to define criteria for each transaction matching.
Step 2: Create exception rules that allow cases outside the identification rule to be set aside.


Step 3: Create exception jobs to qualify and classify anomalies among the exceptions.

@2024 CALIXYS All rights reserved l Privacy policy l Terms and Conditions