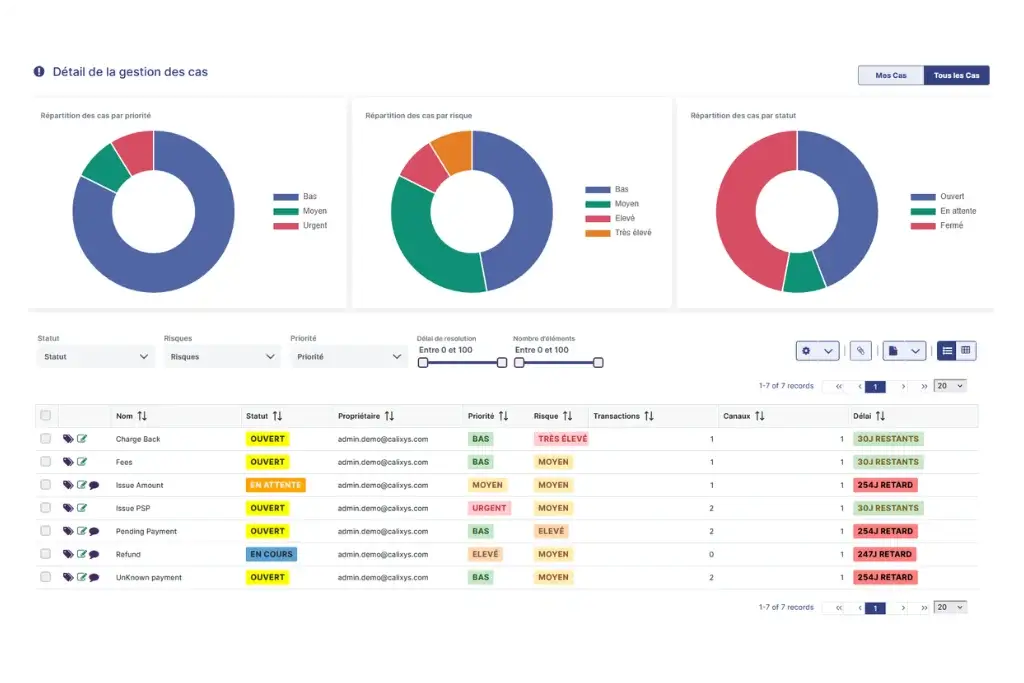
Reconciling Payments at the Cash Register: The Major Challenge for Retailers

Publié
Le 14/05/2024, par :
- Anne Marie Diom
Sections
Contexte
Reconciling Payments at the Cash Register: The Major Challenge for Retailers
Cash Register Reconciliation and Specialised Retail: Definitions
Payment reconciliation involves verifying and aligning financial data across various systems to ensure accuracy and consistency. In the context of physical stores in specialised retail, cash register reconciliation entails comparing actual in-store transactions with the company sales accounting system. This ensures precise correspondence between accounting data and business operations reality. Specifically, each in-store purchase must be traceable in the cash register software, store accounting software, and centralised accounting software at the brand’s headquarters, with all data elements matching (date, product category, store, etc.) to achieve a perfect match. This is the essence of cash payment reconciliation.
Unlike conventional retail, which mainly focuses on food products and general supply sales, specialised retail offers a diverse range of products in specific sectors, often catering to different consumer needs and preferences. Hence, brands in this sector often serve multiple target markets, offering a plethora of product references, thereby increasing reconciliation complexity.
While complex, perfect cash register reconciliation is imperative to limit financial losses. In fact, cumulatively, cash errors incur significant costs. Moreover, the financial health of retailers is at stake, as they have to submit to regular compliance checks. They will be asked to explain any reconciliation discrepancies during regular audits.
Furthermore, despite the automation of payment recording driven by digital purchasing journeys, physical stores maintain a significant market presence. In France, for instance, although consumers are increasingly digital, 91% of purchases still occur in-store (2018 ). Therefore, the position of physical stores in France remains secure amidst digital transformation, making cash register reconciliations an ongoing concern.
In this context of diversified nature of products, multiplication of product references and transactions, the need for precise, smooth, and transparent financial management make cash register reconciliation a complex task with significant stakes.
Payment Reconciliation Errors: the constant headache for specialised retail stores
Volume and Diversity of Data to Process
Cash register reconciliation in physical specialised retail stores is complex due to the large volume of transactions. In 2022, for example, Sephora reported an estimated turnover of €1.26 billion, Decathlon and Darty of €4.7 billion each, and Leroy Merlin of €9.47 billion. With average baskets ranging from 60 to 80 euros in 2023, it indicates the considerable number of transactions these brands handle annually. Managing and reconciling thousands of transactions daily requires a robust and agile accounting system and rigorous organizational protocols.
Additionally, the transition to dematerialised payment methods adds complexity. According to a recent Nielsen study, dematerialised payments, such as credit cards and mobile payments, account for over 60% of transactions in physical stores. This shift, along with “Buy now Pay Later” payments (BNPL), discount codes, and loyalty/gift cards, complicates tracking and reconciling transactions. Cash register reconciliation errors can lead to significant financial losses, representing an average of 2% of stores’ annual turnover, according to the Institute for Retail Research (IRGD).
Disparity of Stores to Reconcile: Centralisation and consolidation of reconciliations
Managing multiple stores across different geographical locations, including international ones, poses additional challenges. Consolidating data from various stores and aligning them with international accounting standards requires meticulous management and effective coordination between financial and operational teams. Establishing a system capable of gathering scattered data from stores worldwide and managing different currencies is essential.
The primary challenge for national and international retail chains is to obtain a 360-degree view of their operations, detecting issues country by country and even store by store. Ideally, they aim for comprehensive, synthetic data while retaining the ability to delve into detailed problem areas. This zoom level and overview are highly sought-after and prove most efficient.
Challenges of payment reconciliation for physical stores: managing diversification
The rise of dematerialised payments and Multichannel Strategies adds new challenges to physical stores of specialised retail in managing their accounting reconciliation.
Dematerialization and diversification of payment methods
According to the European central bank (ECB), transactions made via mobile payment platforms (Apple Pay, Google Pay, etc.) have increased by over 30% in the last year, reflecting a growing trend towards dematerialization.
Dematerialised payment methods, includes credit cards, contactless, mobile payments, and electronic transfers, … These methods offer convenience for consumers but pose challenges for businesses in terms of managing and reconciling payments. The various payment options need to appear in a uniform way, with the same terminology, to make them easier to read. However, the different payment methods mean that a transaction is not necessarily recorded in the exact same way and does not appear at the same time in all software.
Here is a typical example of a card payment made in a physical shop:
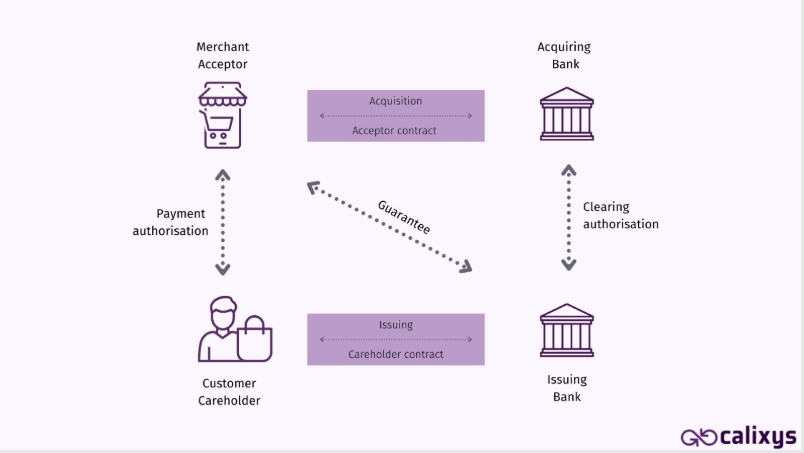
The customer (Cardholder) pays the merchant (Acceptor) in-store using a card. Upon payment, the customer sends the information to their bank and issues a cardholder contract. Then, the customer’s bank first communicates the availability of funds to the merchant (Acceptor) and thus guarantees the transaction. It then requests clearing authorization from the acquiring bank (Merchant’s Bank). Finally, the acquiring bank collaborates with the merchant on an acceptor contract. For a card transaction to be successful, both banks involved must authorise clearing and communicate this guarantee to other stakeholders.
As we can see in this process, the four parties ensure this transaction according to a precise scheme. This scheme/process may vary depending on the method of payment and sales channel. It is therefore evident that managing different payment methods across various purchasing paths increases the difficulties in tracking and reconciling transactions.
Multichannel
Diverse sales channels, such as physical stores, e-commerce websites, and mobile applications, require effective cash register reconciliation to ensure traceability and consistency of financial data. Common purchasing journeys like click & collect, in-store pickup, and drive-through demand integrated transaction management and proper sales attribution.
In conclusion, understanding the challenges associated with cash register reconciliation and adopting appropriate solutions enables companies to overcome obstacles and ensure precise and transparent financial management, contributing to long-term success.
What solutions to address the challenge of optimizing financial management in retail stores ?
Considering the various issues and challenges discussed in this article, several solutions emerge for better cash register reconciliation management:
- Automation: Automation solutions for reconciliation processes streamline operations and reduce the risks of human errors, ensuring efficient management of financial data. In addition to avoiding redundant tasks, automated reconciliations detect discrepancies within a large volume of transactions in record time, enhancing data reliability. By defining precise matching rules, businesses can tailor the software to their operations and ensure the relevance of reconciliations. Finally, automated transaction matching alleviates many challenges faced by specialised stores by handling multi-currency, diverse payment methods, and multichannel strategies.
- Centralization: By centralizing transactions from different sales channels into a single platform, companies can simplify data management and consolidation, providing complete visibility into transactions and financial flows. In addition to simplifying payment reconciliation, data centralization offers additional benefits in terms of advanced analytics, data protection, and data management. The ability to zoom in and have an overview, sought after by businesses, is only possible with complete and effective data centralization. Centralization combined with automation also facilitates real-time visibility, enabling more responsiveness to correct errors and control costs.
- Tracking: Comprehensive traceability and analysis of transactions down to the finest detail enable more informed decision-making and more effective financial management. Information such as purchases made per period, average basket size, sales channel, transaction history, and attempted transactions are precious insights for various business units. Storing transaction history is also essential for research, comparisons, and evolution of financial services.
By understanding the challenges and issues associated with this process and adopting the right solutions, companies can overcome these obstacles and ensure precise and transparent financial management, thereby contributing to their long-term success.
The XREC solution aims to assist companies in their reconciliations. XREC simplifies and harmonises reconciliation and consolidation processes for the retail sector by centralizing cash register reconciliation for each store. This solution automates, accelerates, and facilitates this task by processing a considerable volume of data within seconds. Multicurrency and multichannel, with diverse stores and payment methods, XREC addresses all reconciliation challenges for merchants, offering a transaction matching rate of 99.9%! XREC is a Cloud-based SaaS solution developed by Calixys, integrating seamlessly with your accounting processes.